E’ una variante dell’ accesso chirurgico anteriore mini-invasivo con incisione longitudinale. E’ anche definita “Bikini” perchè l’ incisione viene praticata lungo la plica inguinale facilmente identificabile flettendo l’ anca. Differisce dalla tradizionale soltanto nell’ incisione che è obliqua mentre nei piani sottostanti la cute la procedura è identica. E’ esteticamente più gradevole ma anche vantaggiosa dal punto di vista pratico perchè cade esattamente a metà del campo operatorio. Può essere adottata indifferentemente nei due sessi. In mani esperte è altrettanto affidabile della longitudinale coniugando in più estetica e praticità. Nella nostra esperienza ha dato ottimi risultati e dal 2011 è diventata una tecnica standard che utilizziamo anche in persone obese.
It is a of the minimally invasive anterior surgical access with longitudinal incision. It is also called “Bikini” because the incision is made along the easily identifiable inguinal fold by flexing the hip. It differs from the traditional one only in the incision which is oblique while in the planes below the skin the procedure is identical. It is aesthetically more pleasant but also advantageous from a practical point of view because it falls exactly in the middle of the operating field. It can be adopted indifferently in both sexes. In expert hands it is just as reliable as the longitudinal, combining aesthetics and practicality. In our experience it has given excellent results and since 2011 it has become a standard technique that we also use in obese people.
Anca destra, repere cutaneo lungo la plica inguinale: con matita dermografica si traccia una linea obliqua lungo la plica inguinale facilmente identificabile flettendo l’anca. Evitare di prendere come riferimento le pliche inguinali più distali, se presenti.
Right hip, skin landmark along the inguinal fold: with a dermographic pencil, an oblique line is drawn along the inguinal fold, easily identifiable by flexing the hip. Avoid referencing the more distal inguinal folds, if any.
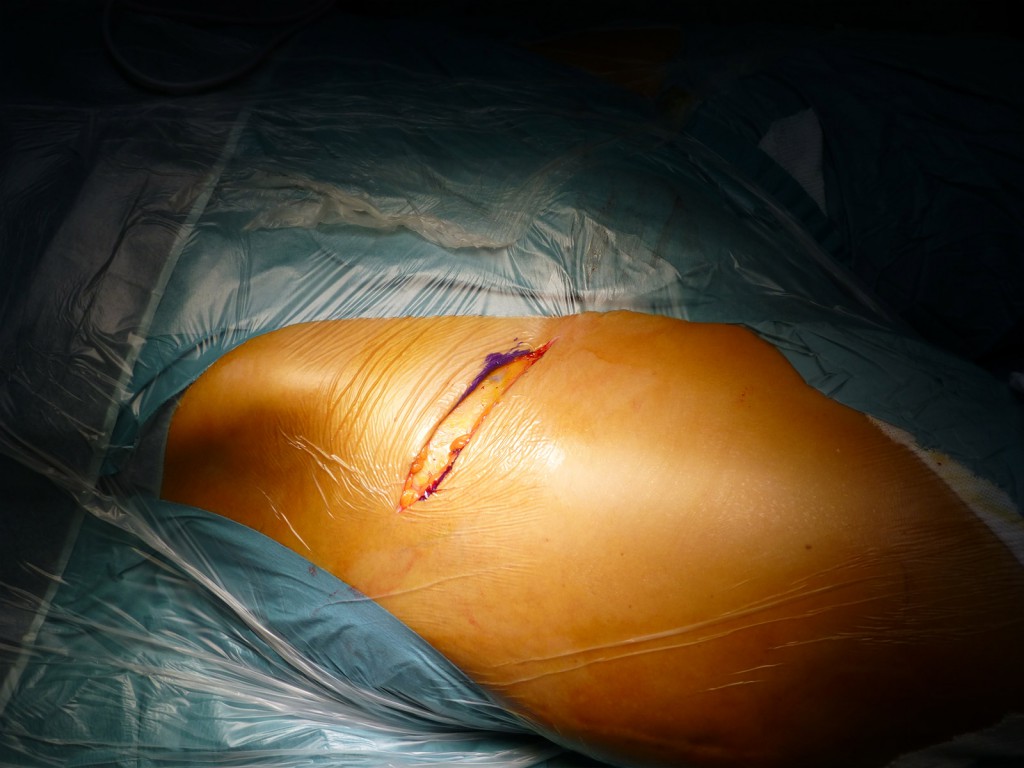
Incisione cute e sottocute: la lunghezza varia in rapporto al BMI ed è in genere tra i 5 e 8 cm. Spesso si è portati a stare più caudali ma il punto esatto è più prossimale e cade a non più di 2 dita traverse dalla SIAS. Per evitare lacerazioni della ferita durante la divaricazione è consigliabile dare un punto di sutura di arresto sulla cute nel tratto mediale. E’ l’ ultimo passaggio che avviene su un piano obliquo. Tutte gli step successivi avvengono in senso longitudinale.
Skin and subcutaneous incision: the length varies in relation to the BMI and is generally between 5 and 8 cm. Often it is brought to stay more caudal but the exact point is more proximal and falls no more than 2 fingers traverse from the ASIS. To avoid lacerations of the wound during retraction it is advisable to give a stop suture on the skin in the medial tract. It is the last step that takes place on an oblique plane. All subsequent phases take place in a longitudinal direction.
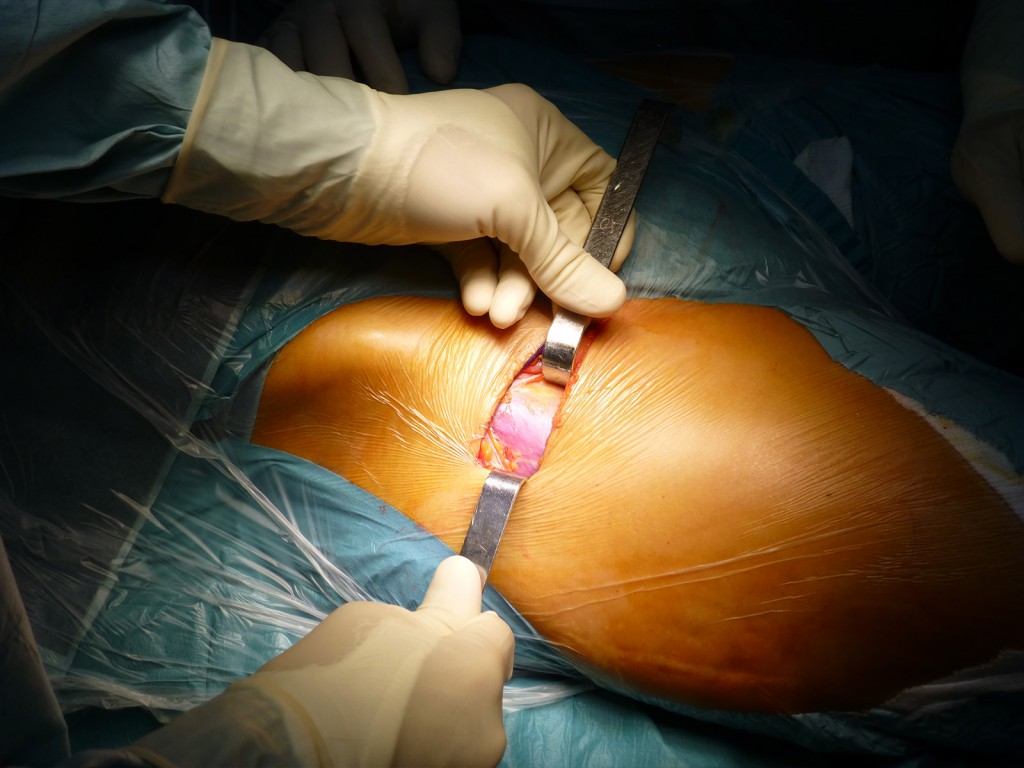
Esposizione aponeurosi tensore fascia lata (TFL): per via smussa si scolla il tessuto adiposo dalla fascia del TFL al di sotto della quale traspaiono le fibre del muscolo orientate lungo l’ asse longitudinale della coscia. Se sono oblique lateralmente sono quelle del muscolo medio gluteo (Accesso di Rottinger) se medialmente sono quelle del sartorio (Accesso di Smith Petersen).
Exposure of aponeurosis tensor fascia lata (TFL): the adipose tissue is blunted from the fascia of the TFL under which the muscle fibers oriented along the longitudinal axis of the thigh transpire. they are oblique laterally they are those of the gluteus medius muscle (Rottinger’s approach) if medially they are those of the sartorius (Smith Petersen’s approach).
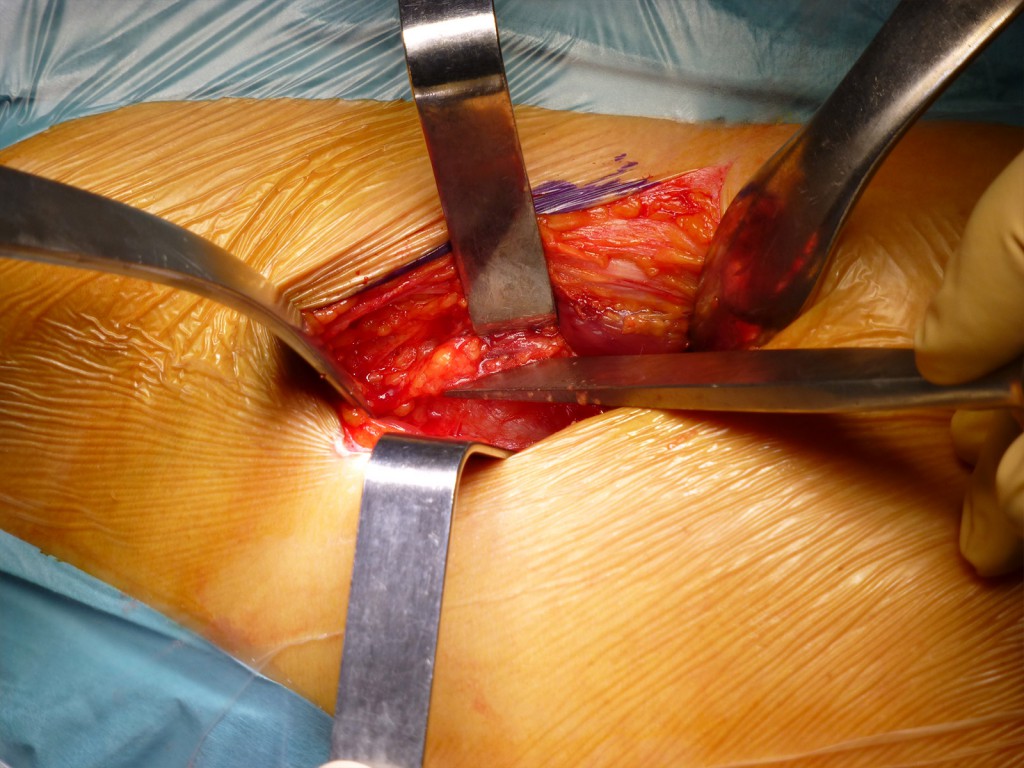
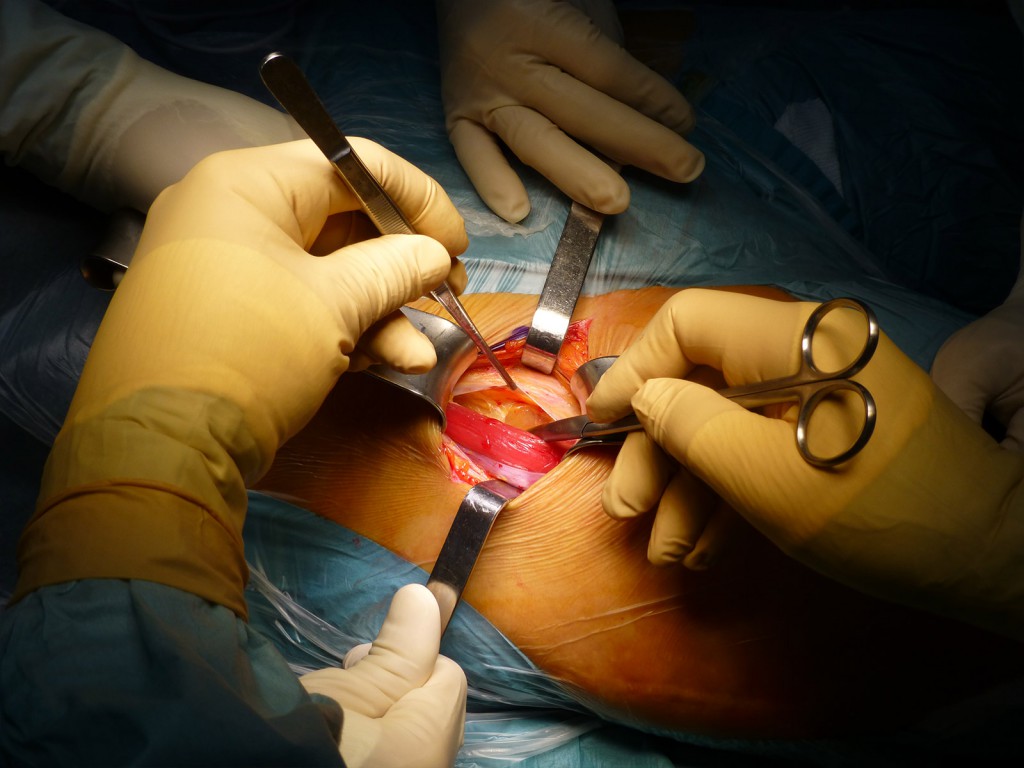
Divaricazione cranio-caudale della ferita e ricerca repere anatomico del TFL: Mediante l’ utilizzo di 2 Farabeuf e due divaricatori ad orecchio si completa la esposizione del campo. E’ ben visibile la direzione longitudinale delle fibre muscolari del TFL. Una piccola arteria , costantemente presente, perfora il TFL e si dirige nel sottocute. Origina dalla branca ascendente dell’ arteria circonflessa anteriore e si rinviene nel tratto dorsale del campo operatorio. Identifica con certezza il muscolo TFL.
Cranio-caudal retraction of the wound and anatomical reference search of the TFL: The exposure of the field is completed by using 2 Farabeufs and two ear retractors. The longitudinal direction of the TFL muscle fibers is clearly visible. A small, constantly present artery pierces the TFL and goes into the subcutis. It originates from the ascending branch of the anterior circumflex artery and is found in the dorsal tract of the operative field. Identify with certainty the TFL muscle.
Incisione del perimisio del TFL: Con il bisturi si incide delicatamente il perimisio del TFL prolungando l’ incisione, se necessario, in direzione prossimale e distale con forbici.
Incision of the perimysium of the TFL: With the scalpel, the perimysium of the TFL is gently incised, extending the incision, if necessary, proximally and distally with scissors.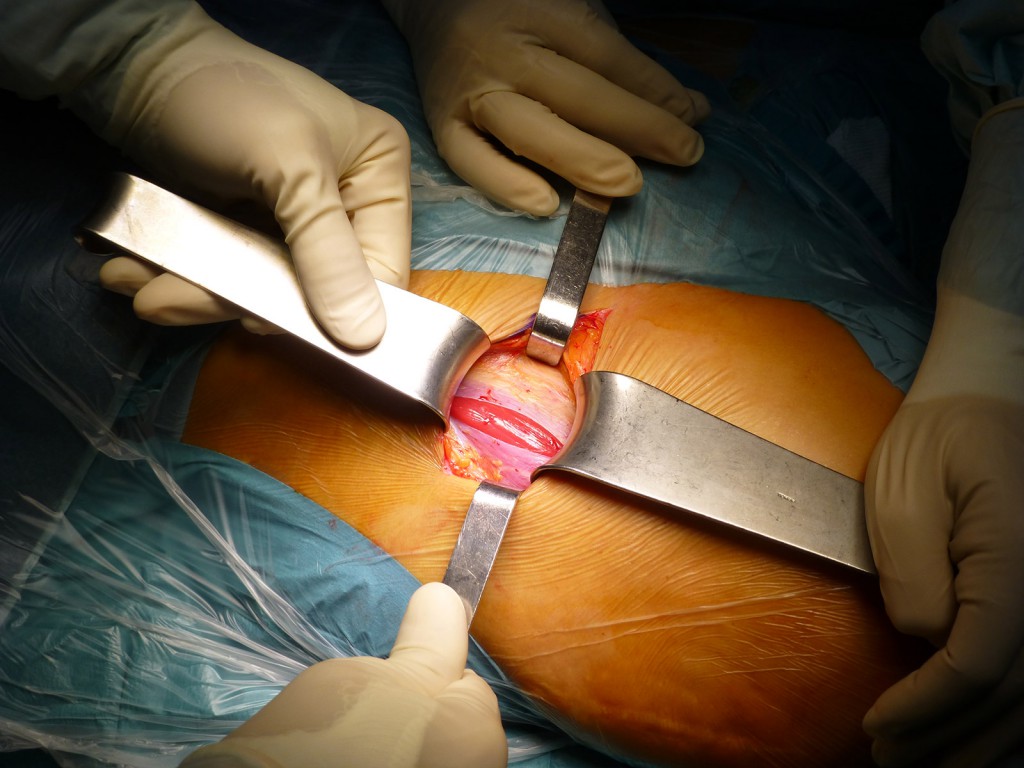
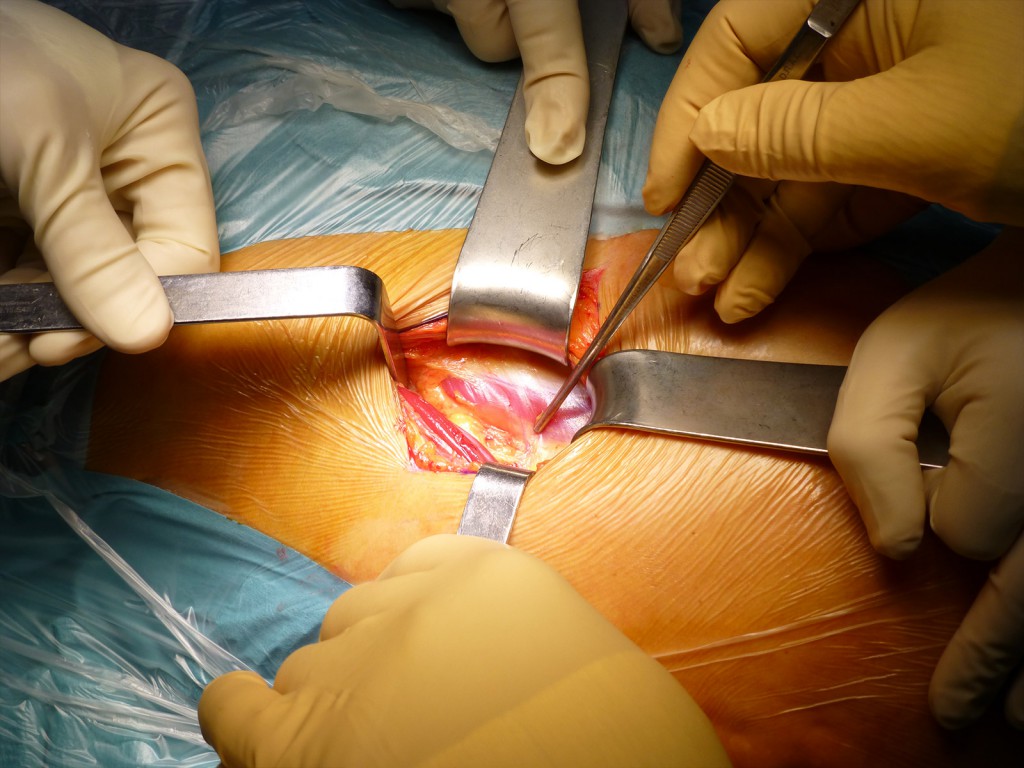
Scollamento del TFL dal perimisio ed esposizione interspazio TFL-Retto Ant: Per via smussa si scolla il TFL dal permisio , sollevato con pinza e dislocato lateralmente.
Detachment of the TFL from the perimysium and exposure of the TFL-Rectus Ant: By blunt way, the TFL is detached from the permisium, lifted with pliers, and displaced laterally.
Le tre zone Rosso-Giallo-Rosso: Lateralizzato il muscolo TFL si espone l’ interstizio con il Retto Anteriore. E’ evidente la banda tricolore costituita dal TFL lateralmente, il tessuto adiposo dell’ interstizio ed il Retto Anteriore. Una piccola arteria perforante che penetra nel Retto Anteriore è indicata da una pinza chirurgica.
The three zones Red-Yellow-Red: Lateralized the TFL muscle exposes the interstitium with the Anterior Rectum. The tricolor band constituted by the TFL laterally, the adipose tissue of the interstitium and the Anterior Rectum are evident. A small perforating artery that penetrates the Anterior Rectum is indicated by the surgical forceps.
Dettaglio della figura precedente: la pinza indica l’ arteriola che verrà coagulata.
Detail of the previous figure: the surgical forceps indicate the arteriole that will be coagulated. 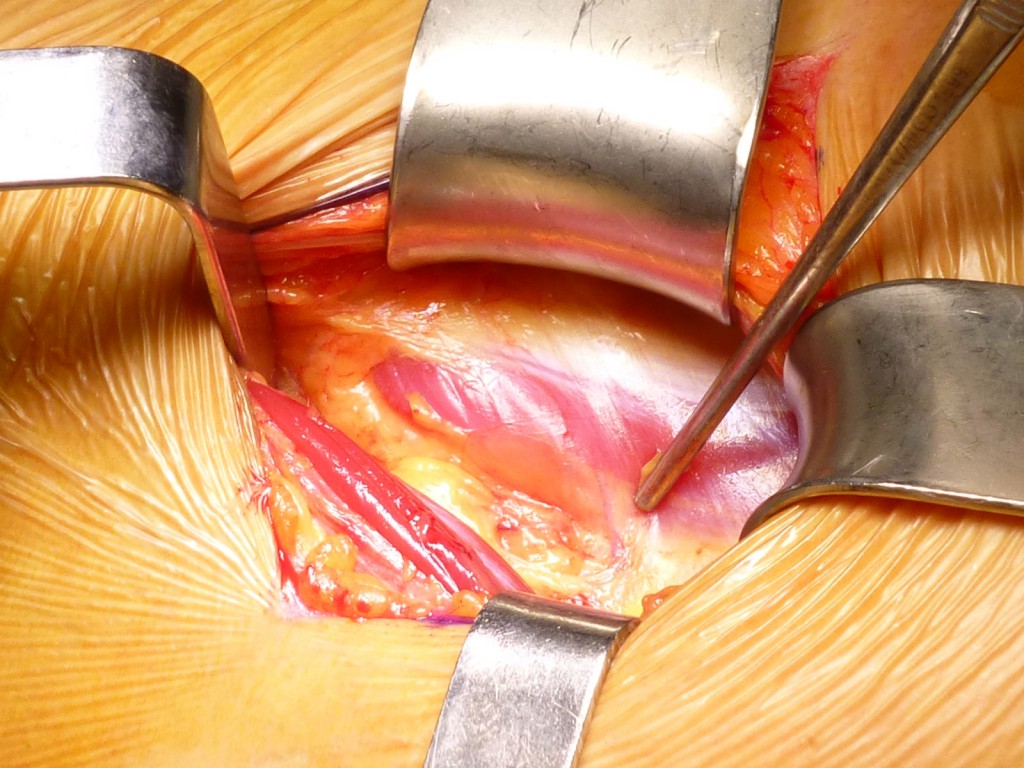
Sezione del perimisio del Retto Anteriore: con il bisturi si seziona delicatamente il perimisio del Retto Anteriore.
Section of the perimysium of the anterior rectum: with the scalpel, the perimysium of the anterior rectum is gently sectioned.
Esposizione della aponeurosi innominata: Il Retto anteriore è caricato mediamente su un Farabeuf . Si espone la sottile aponeurosi innominata. Sotto di essa traspare nel tratto distale del campo operatorio l’ arteria circonflessa anteriore. Decorre obliqua in senso latero-mediale e parallela alle fibre del muscolo vasto laterale.
Exposure of the innominate aponeurosis: the anterior rectum is medially loaded on a Farabeuf. The subtle innominate aponeurosis is exposed. Under it, in the distal section of the operative field, anterior circumflex artery transpires. Runs oblique in a latero-medial direction and parallel to the fibers of the vastus lateral muscle.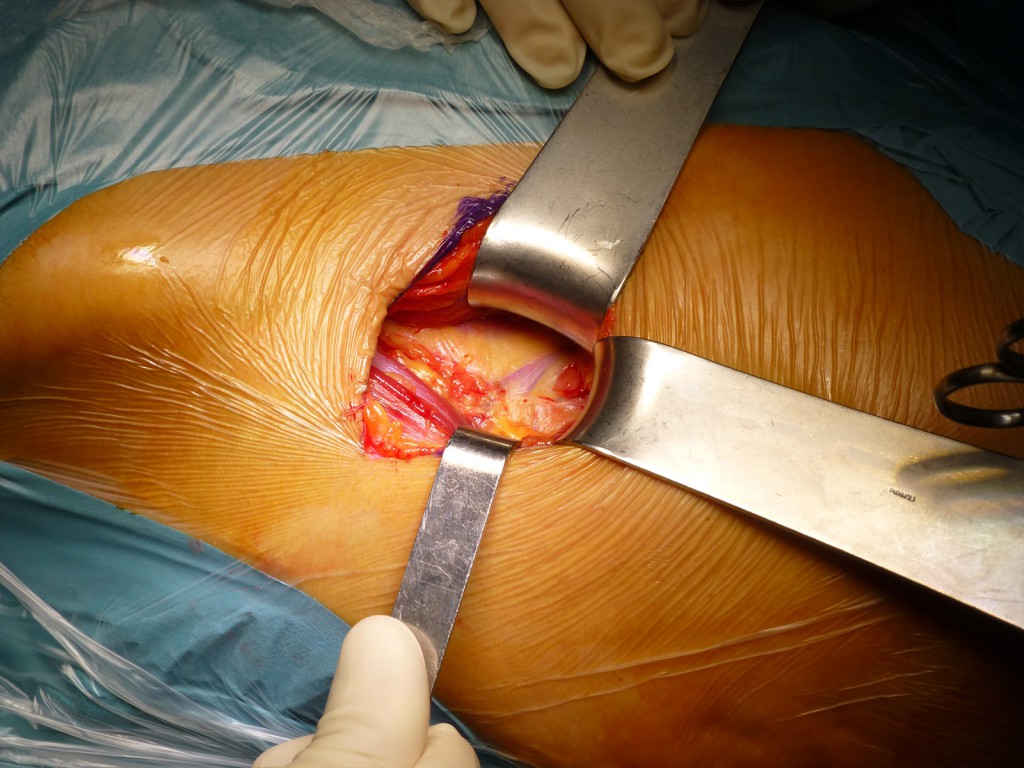
Sezione dell’ aponeurosi e legatura della arteria circonflessa: Si seziona con delicatezza l’ aponeurosi per non ledere la sottostante arteria che viene isolata e sezionata tra due lacci. E’ consigliabile legare il vaso perchè se coagulato potrebbe sanguinare a caduta del coagulo. I lacci vengono lasciati un po’ lunghi per essere identificabili a fine intervento e poter verificare che non ci siano perdite dall’ arteria. E’ visibile al di sotto dell’ arteria il tessuto adiposo precaspulare.
Section of the aponeurosis and ligation of the circumflex artery: The aponeurosis is delicately dissected in order not to damage the underlying artery which is isolated and sectioned between two laces. It is advisable to tie the vessel because if it coagulates it could bleed when the clot falls. The laces are left a little long to be identifiable at the end of the surgery and to be able to check that there are no leaks from the artery.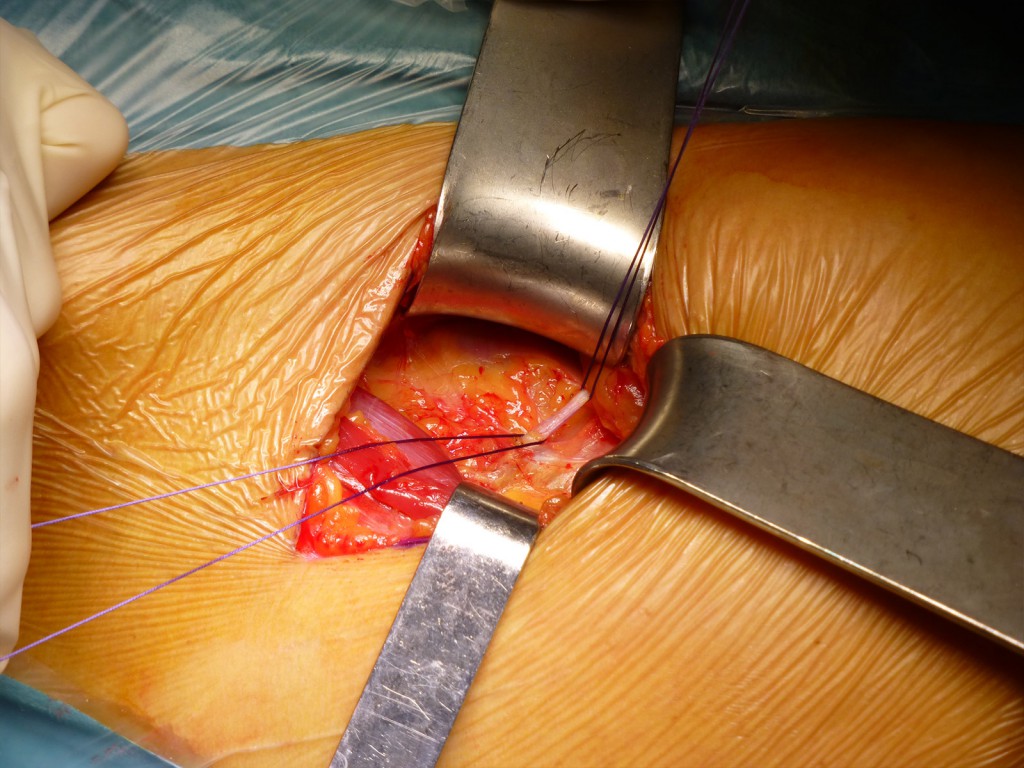
Esposizione del piano precapsulare: Legata l’ arteria si espone il grasso precapsulare e l’ inserzione prossimale del muscolo vasto laterale.
Exposure of the precapsular plane: When the artery is tied, the precapsular fat and the proximal insertion of the vastus lateral muscle are exposed.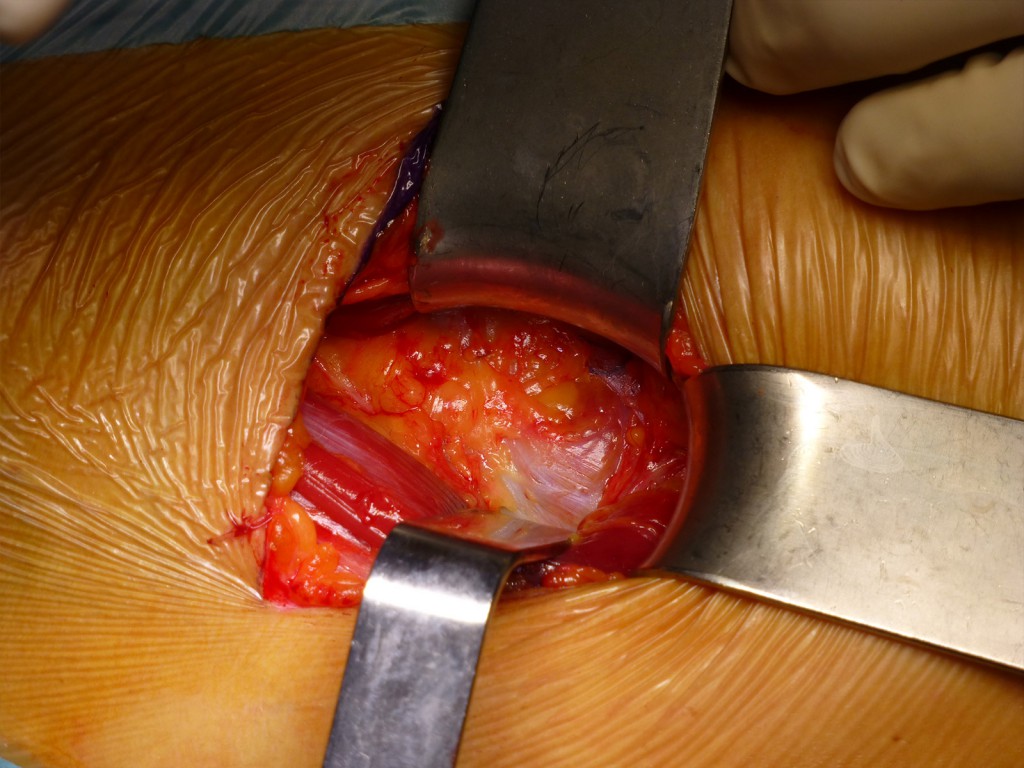
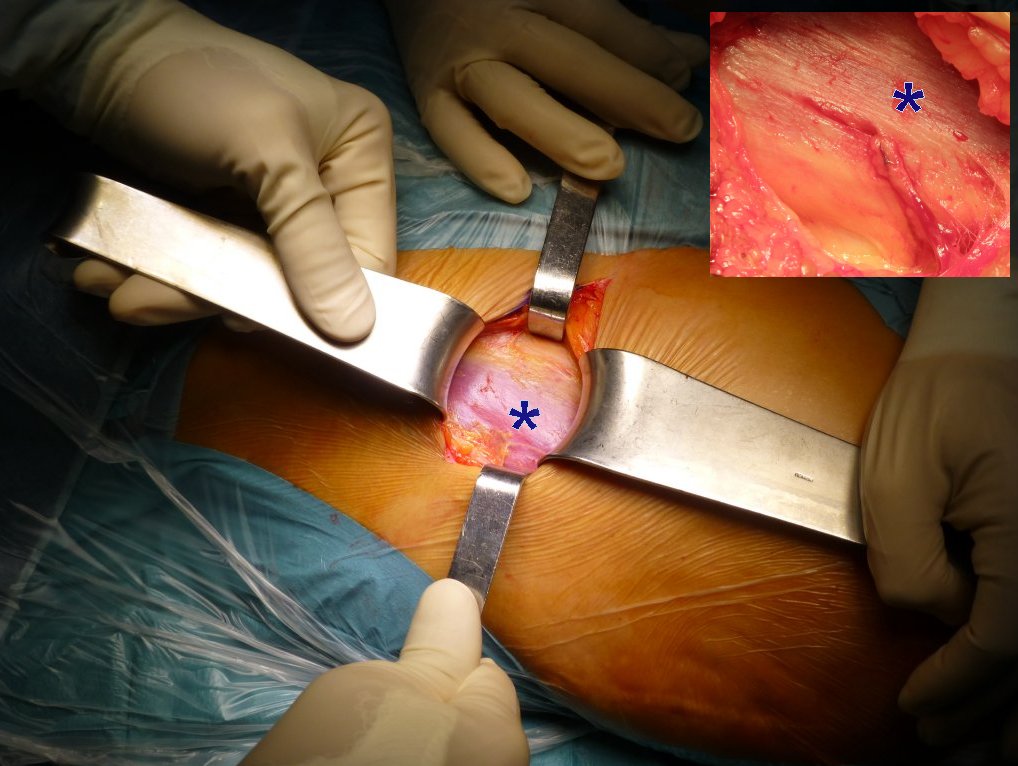
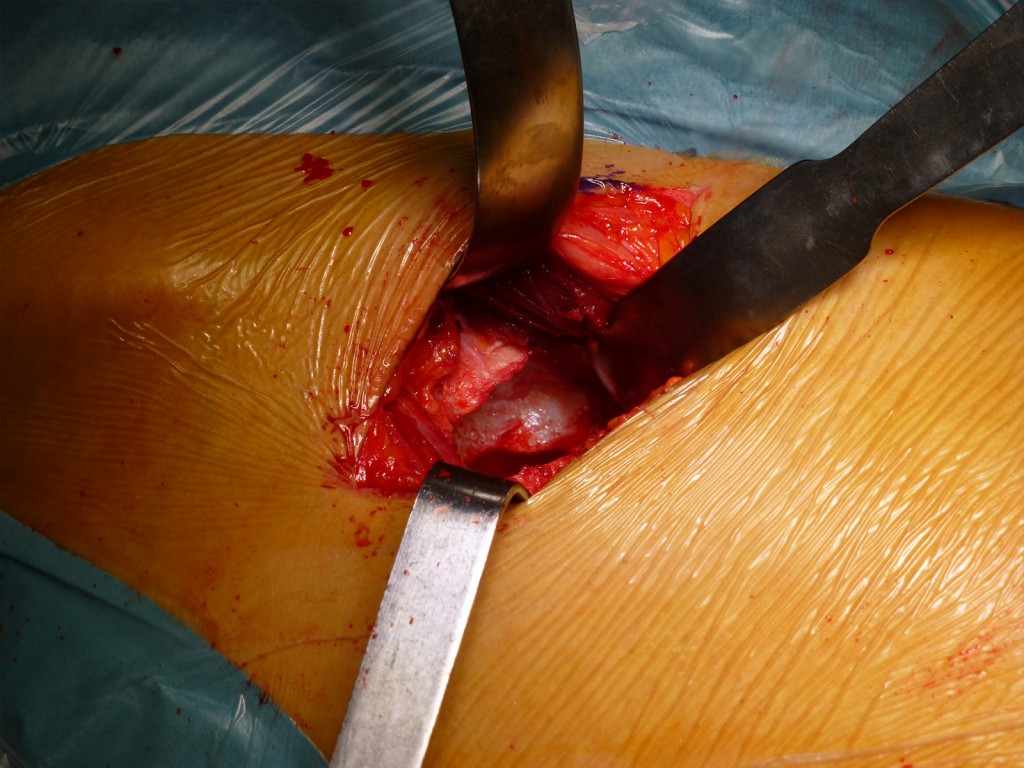
Esposizione della capsula: Con scalpello o scollatore si elimina il grasso precapsulare e si espone la capsula.
Exposure of the capsule: With a chisel or peeler, the precapsular fat is removed and the capsule is exposed.
Tempo accessorio: la buona visuale che l’ accesso consente, una volta rimossa la testa femorale, permette anche l’ asportazione dell’ osteofita anteriore.
Esposizione acetabolo: Strumenti utilizzati: 2 Farabeuf, 1 Hohmann. Notare il campo pressoché esangue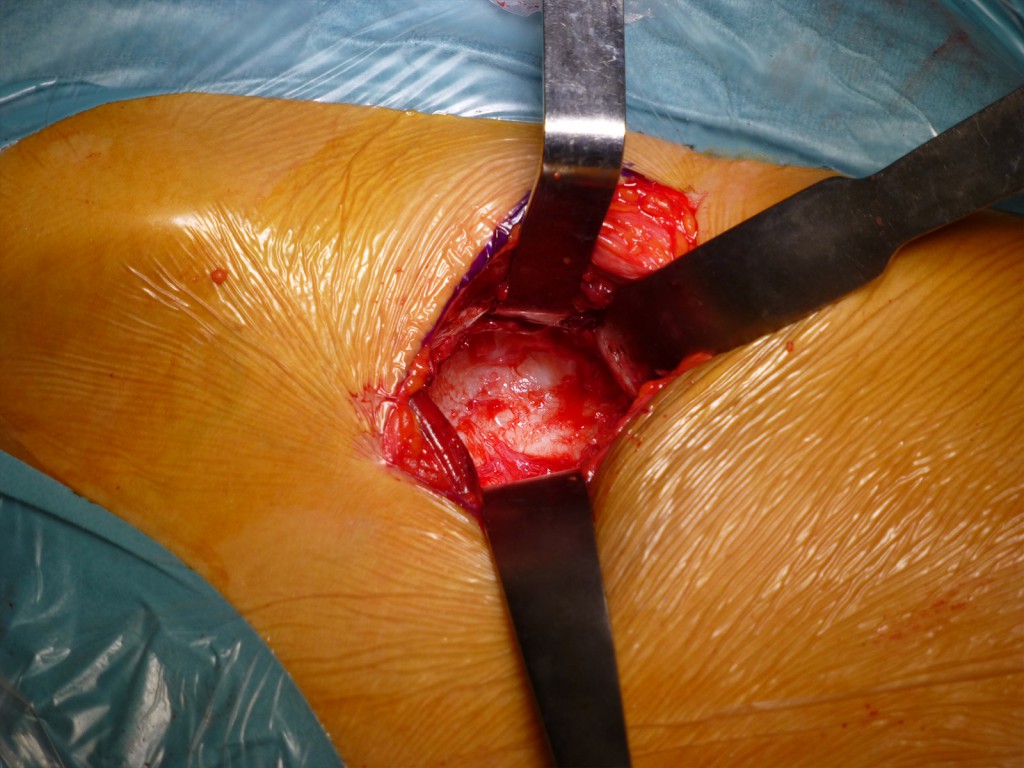
Esposizione femore: Nonostante l’ esiguità dell’ accesso il femore può essere esposto quanto basta per poter inserire lo stelo.
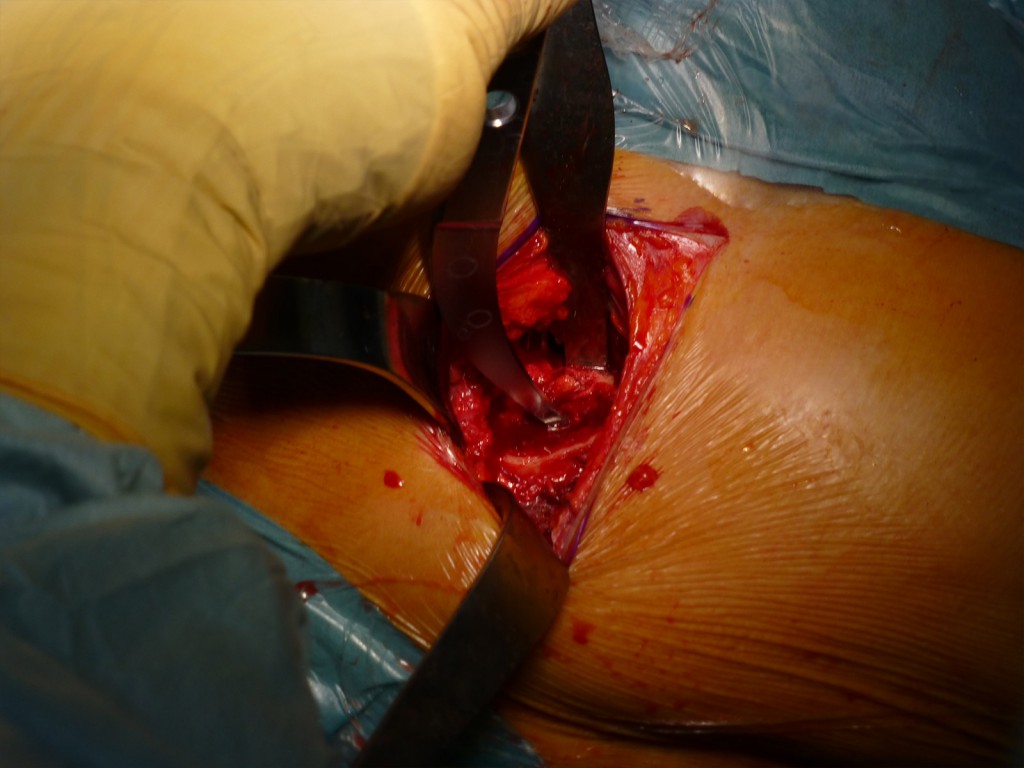
Tempo finale: notare in basso nella ferita chirurgica il TFL continuo e appena al disopra la loggia del M. Sartorio (dove decorre il N. Femoro Cutaneo) perfettamente intatta.
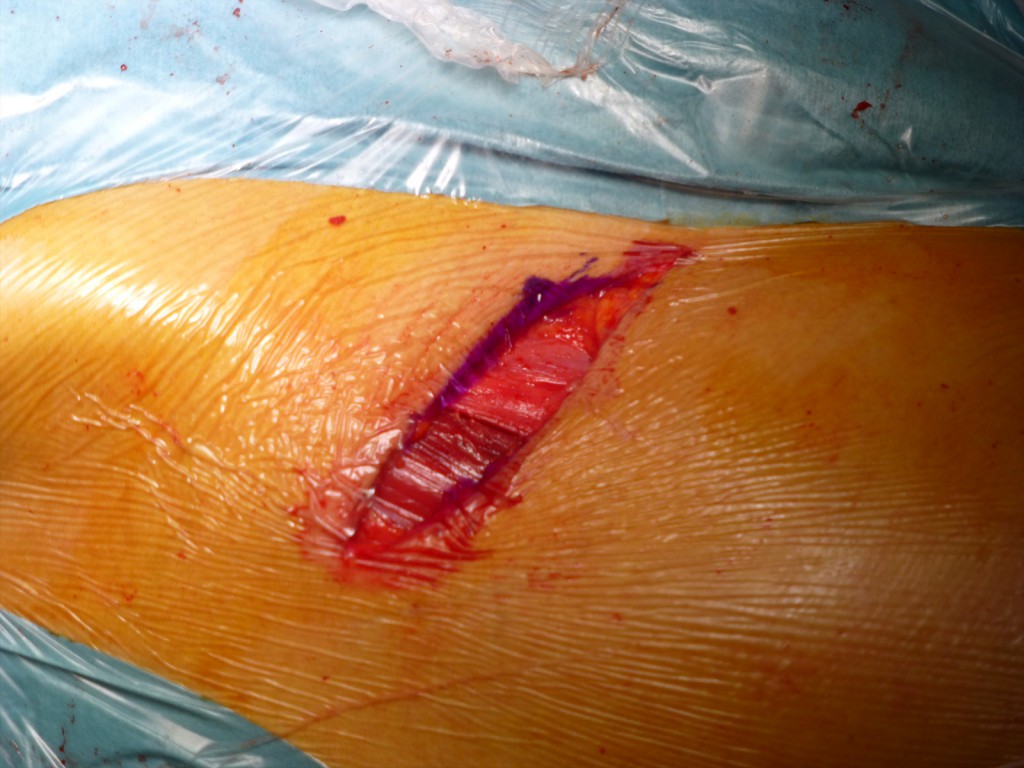
Sutura della cute: Chiusura della ferita con punti intradermici.
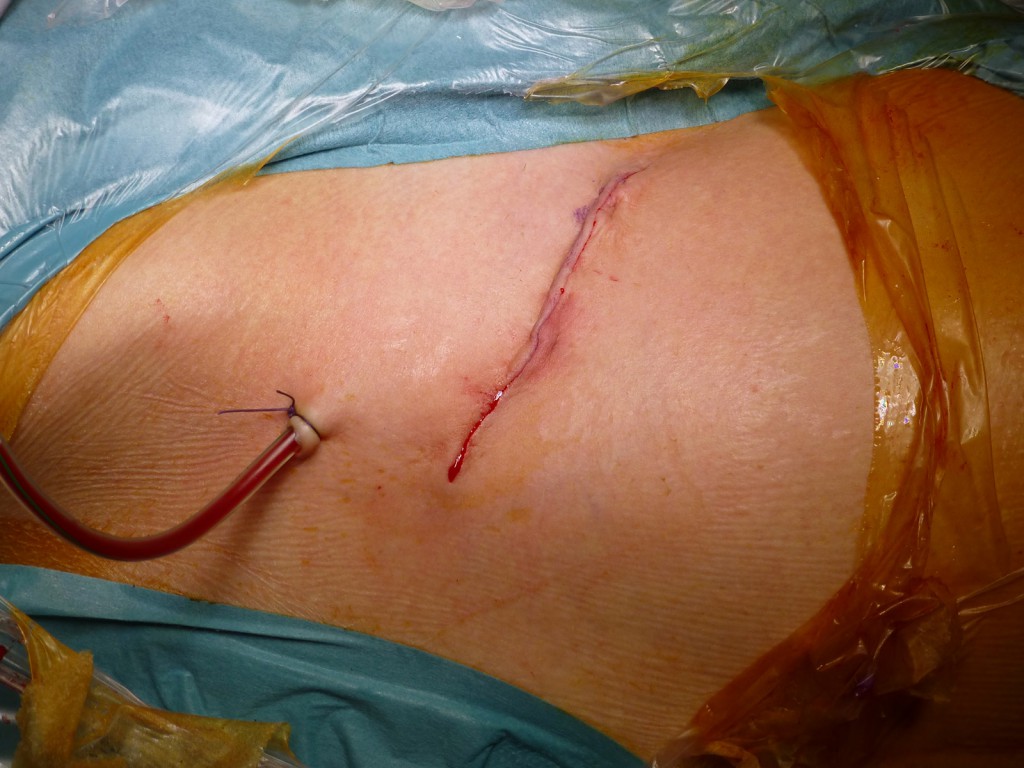
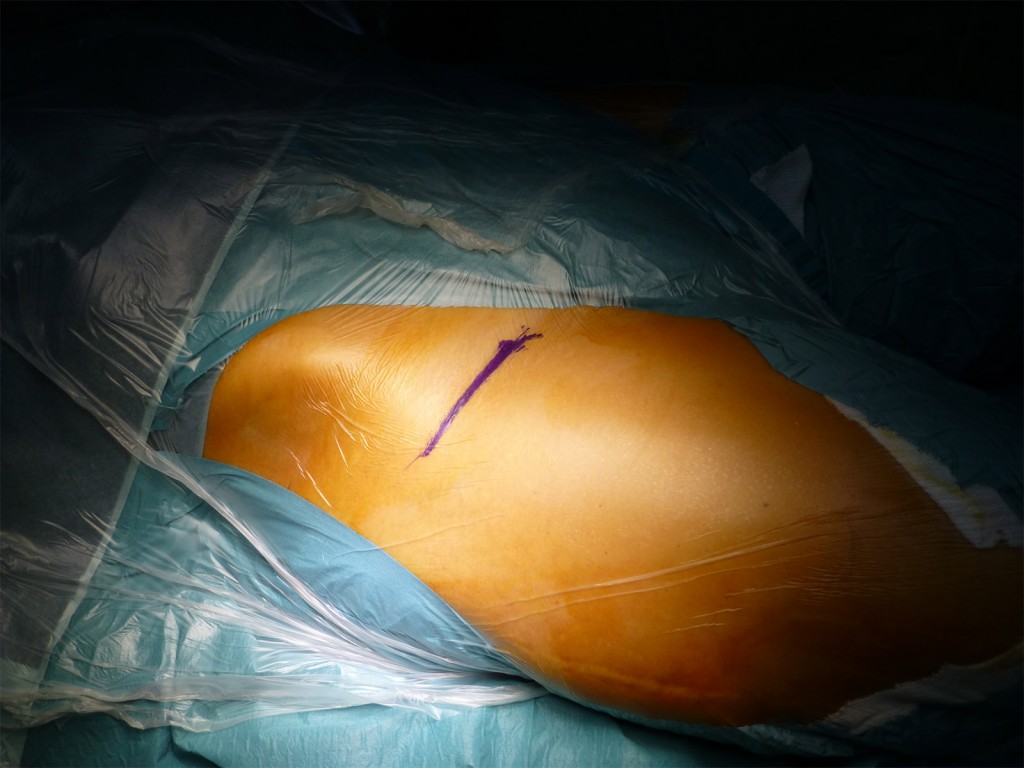
Aspetto finale: Appena visibile la cicatrice chirurgica di appena 7-8 cm. Guarisce perfettamente perchè la cute è poco traumatizzata e perchè l’ accesso chirurgico non attraversa le linee di Langer. E’ agevolmente nascondibile sotto gli slip. 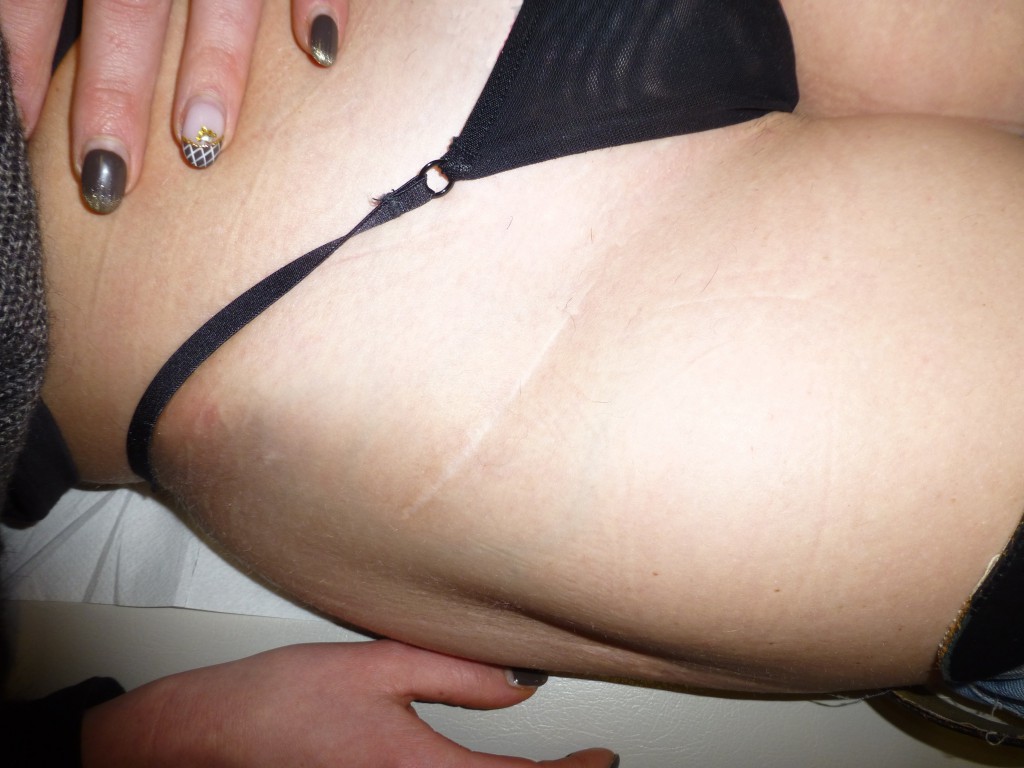
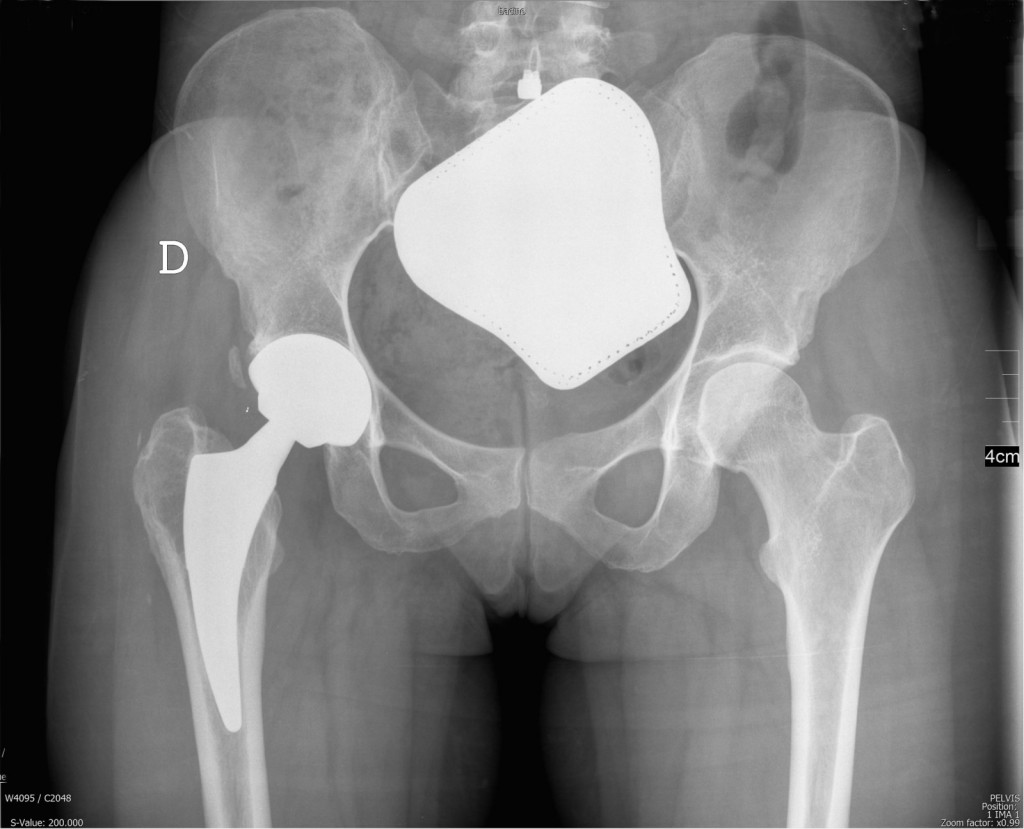
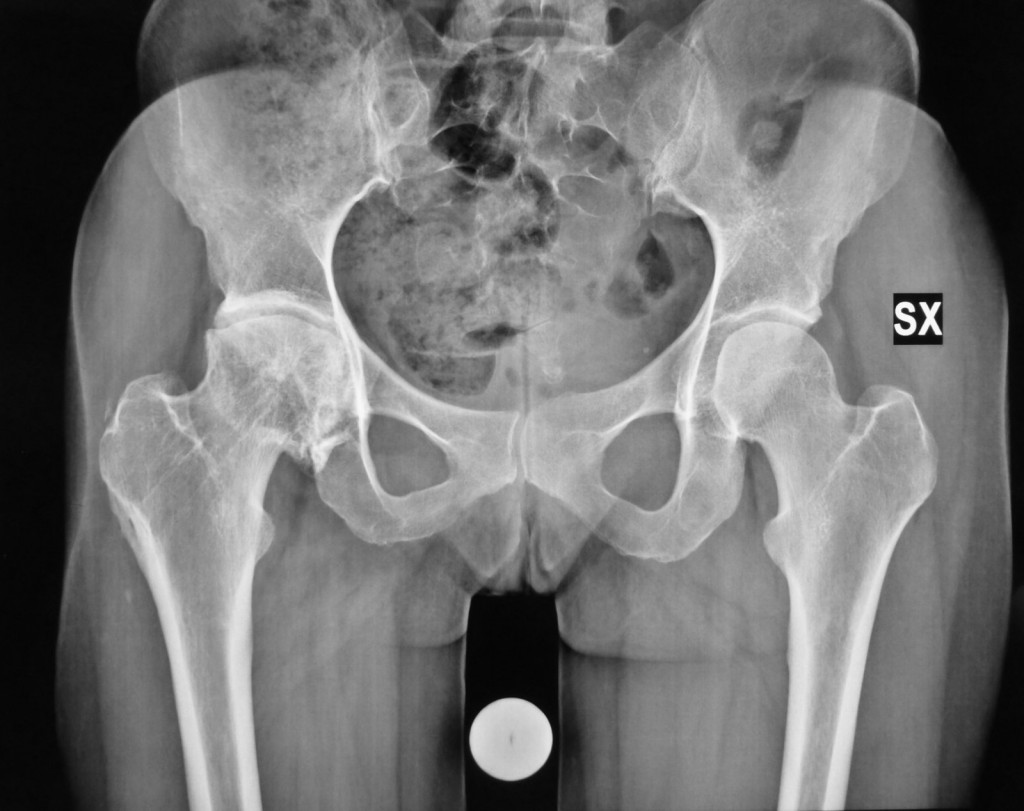
Quadro radiografico preoperatorio: Coxartrosi dx postraumatica in giovane donna
Controllo radiografico postopertorio: Buon posizionamento della protesi d’ anca.